Transformer tap changer
Transformer voltage regulation is to set a tap on a certain winding of the transformer. When the tap is changed, a part of the wire turns is reduced or increased, so that the number of turns of the transformer winding with the tap is reduced or increased, and the number of turns of other windings does not change, thereby changing the turns ratio of the transformer winding. When the turns ratio of the winding changes, the voltage ratio also changes accordingly, and the output voltage changes, thus achieving the purpose of adjusting the voltage.
In general, appropriate taps are pulled out from the high-voltage winding, because the high-voltage winding is often placed outside, making it convenient to lead out the taps; in addition, the current on the high-voltage side is small, the cross-sectional area of the tap leads and the current-carrying part of the tap changer is small, and the switch contact part is also easy to solve.
There are two types of voltage regulation: no-excitation voltage regulation and on-load voltage regulation. In no-excitation voltage regulation, the transformer secondary is not unloaded, but both sides of the transformer are disconnected from the power grid, and the tap of the winding is changed when the transformer is not excited; in on-load voltage regulation, the transformer changes the tap of the winding without interrupting the load.
The rated voltage range of the off-excitation tap changer of the transformer is narrow, and the number of adjustment levels is small. The rated voltage adjustment range is expressed as a percentage of the rated voltage of the transformer as ±5% or ±2×2.5%. According to the use requirements, it is allowed to increase the number of negative taps and reduce the number of positive taps while the voltage adjustment range and the number of levels remain unchanged. When the off-excitation voltage-regulating transformer changes the tap position within the rated voltage ±5%, its rated capacity remains unchanged. If it is -7% and +10% tapping, its capacity shall be in accordance with the manufacturer’s regulations; if there is no manufacturer’s regulations, the capacity shall be reduced by 2.5% and 5% accordingly.
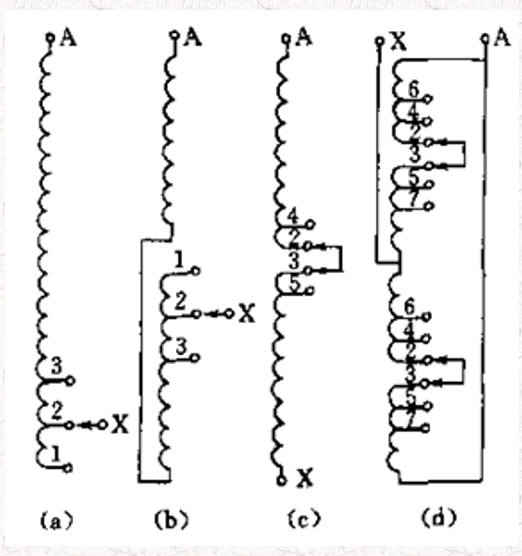
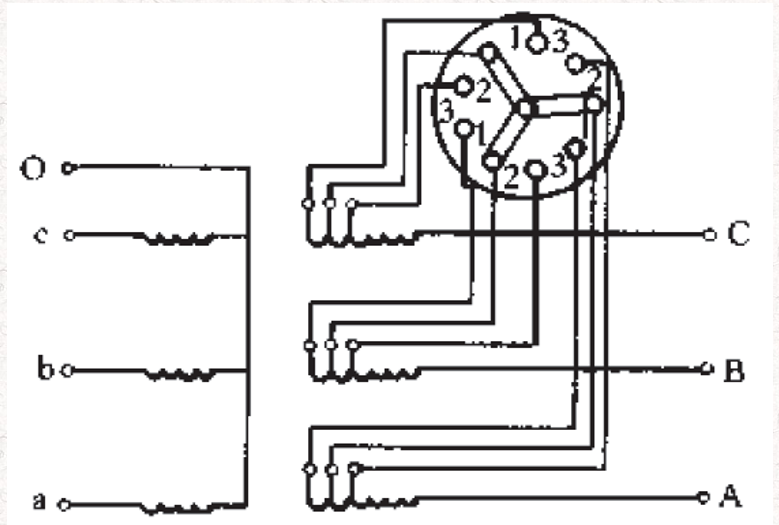
The transformer non-excitation voltage regulation circuit has four general types due to the different ways of tapping the winding:
1) Neutral point voltage regulation circuit, generally applicable to multi-layer cylindrical windings with voltage levels of 35KV and below;
2) Neutral point “reverse connection” voltage regulation circuit, applicable to connected windings with voltage levels of 15KV and below;
3) Middle voltage regulation circuit;
4) Middle parallel voltage regulation circuit, applicable to continuous or tangled windings with voltage levels of 35KV and above.
Post time: Jul-28-2025