Active power filters are primarily used to dynamically filter harmonics and compensate for reactive power, improving power quality and equipment reliability. They detect and compensate for harmonic currents in real time, making the current injected into the grid closer to a sine wave, thereby reducing the impact of harmonics on the grid and power-consuming equipment.
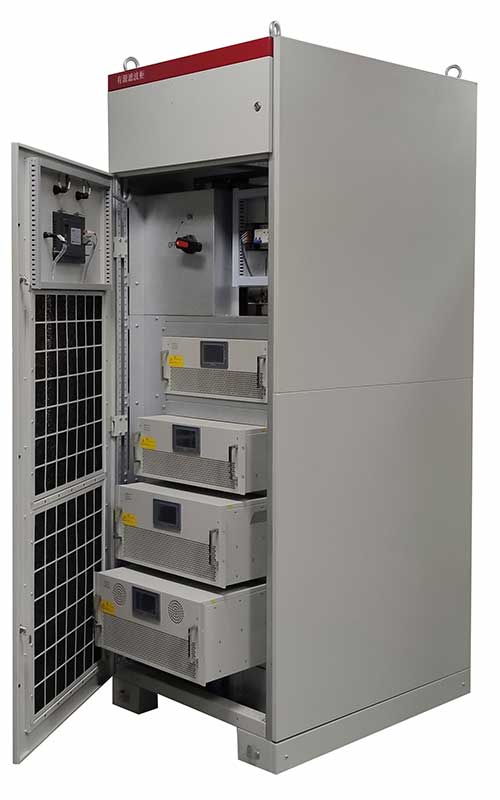

Active power filters are primarily used for compensation in the following areas:
Harmonic Control:
Active power filters effectively filter various harmonics generated by nonlinear loads, such as the third, fifth, and seventh harmonics. This reduces harmonic interference with equipment, reduces heat generation and insulation degradation, and extends equipment life.
Reactive Power Compensation:
Active power filters dynamically provide or absorb reactive power, improving power factor, reducing reactive power losses, increasing grid utilization, and reducing electricity bills.
Improving Power Quality:
By filtering harmonics and compensating for reactive power, active power filters improve grid voltage quality, reduce voltage fluctuations and flicker, ensure stable equipment operation, and avoid equipment malfunctions and downtime caused by voltage issues. Reduced Equipment Maintenance Costs:
By reducing harmonic interference and improving grid quality, active power filters can reduce equipment failure rates, extend equipment life, and thus lower maintenance costs.
Meeting National Standards:
Many countries and regions have strict standards for grid harmonic content and reactive power. The use of active power filters can help companies meet these standards and avoid fines and legal liability.
Compared to traditional filters, active power filters offer the following advantages:
Dynamic Compensation:
Active power filters can track load changes in real time and dynamically adjust compensation currents, while traditional filters typically use static compensation and have poor adaptability to load changes.
High-Precision Compensation:
Active power filters achieve high-precision harmonic filtering and reactive power compensation, while traditional filters may suffer from under- or over-compensation in certain situations.
Wide Applicability:
Active power filters can adapt to a variety of complex grid environments and load types, while traditional filters may be limited by grid parameters and load characteristics.
In summary, the use of active power filters can significantly improve power quality, reduce equipment maintenance costs, and increase equipment operating efficiency, making them a crucial power electronic device in modern power systems.
Post time: Jul-31-2025