Distribution panels can be categorized in various ways based on different standards, primarily by voltage level, structural features, installation method, and location.
1. By Voltage Level:
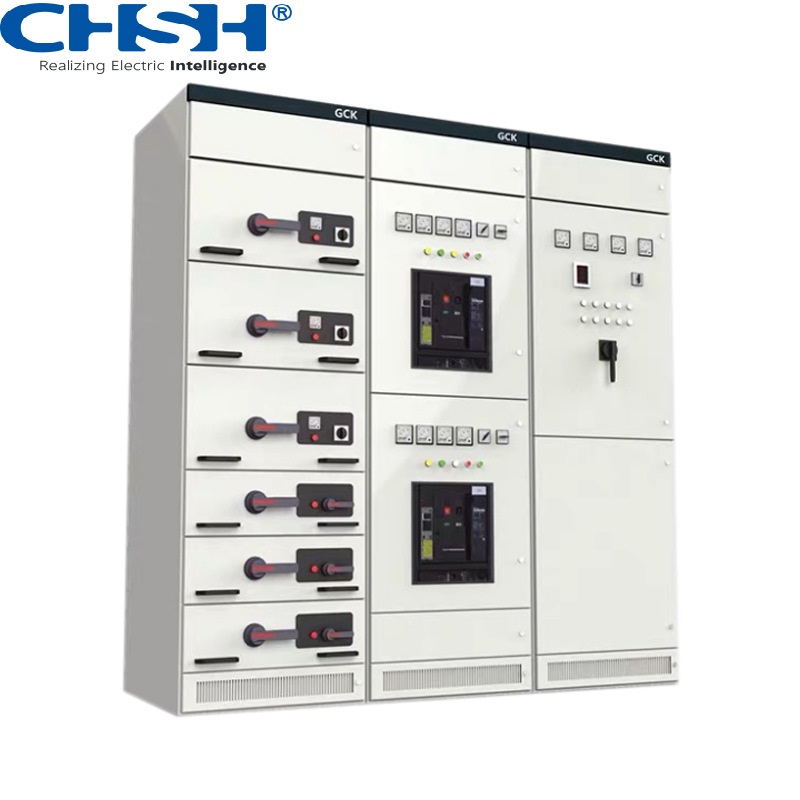
• Low-voltage distribution panels: Typically refers to distribution panels rated at 1 kV or below, used to distribute lower voltage power.

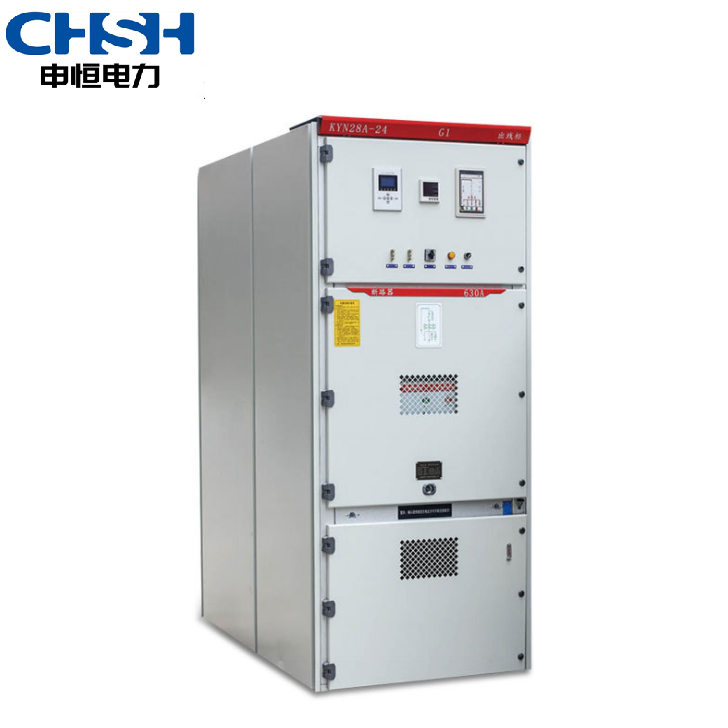
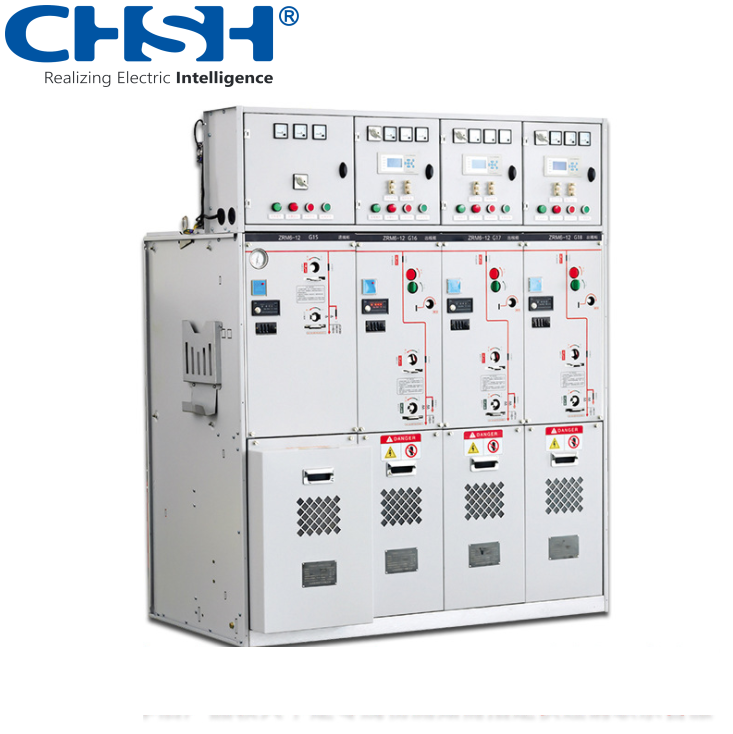
• Medium-voltage distribution panels: Refers to distribution panels rated between 3 kV and 35 kV, also often referred to as high-voltage switchgear.
• High-voltage distribution panels: Typically refers to distribution panels rated at 35 kV or higher, but above 35 kV, GIS-type switchgear are often used.
2. By Structural Features:
• Fixed distribution panels: Components are fixedly installed within the panel, making maintenance inconvenient but operating reliably and stably.
• Drawer-type distribution panels: Components are installed in removable drawers, making maintenance and replacement easier, but requiring more primary and secondary circuit connections.
• Metal-enclosed armored switchgear: The panel has a metal enclosure with a compartmentalized or armored structure, offering enhanced safety.
• Metal-enclosed box-type fixed switchgear: The cabinet has a metal-enclosed, box-type structure and is suitable for various applications.
3. By Installation Method:
• Fixed switchgear: Components are fixedly installed in the cabinet.
• Removable (trolley-type) switchgear: Components such as circuit breakers can be removed for maintenance and replacement.
• Floor-standing switchgear: In trolley-type switchgear, the trolley is installed at the bottom of the cabinet.
• Center-mounted switchgear: In trolley-type switchgear, the trolley is installed in the middle of the cabinet.
4. By Location:
• Indoor distribution cabinet: Suitable for indoor installation.
• Outdoor distribution cabinet: Suitable for outdoor installation, typically featuring waterproof and dustproof features.
5. Other Categories:
• By Main Wiring Type: Such as bridge wiring, single busbar, double busbar, etc.
• By Circuit Breaker Type: Such as air circuit breakers, SF6 circuit breakers, etc.
• By Insulation Medium: Such as air insulation, SF6 gas insulation, etc.
• By function: such as power distribution cabinets, motor control centers, lighting distribution boxes, etc.
Common model examples:
• Low voltage: GGD (fixed type), GCK, GCS, MNS (drawer type).
• High voltage: KYN28A-12 (indoor type), XLW (outdoor type).
The selection of a distribution cabinet requires comprehensive consideration based on the specific application scenario, electrical parameters, installation environment, and other factors.
Post time: Aug-11-2025